Food Traceability Market Research Report: By Equipment (PDA with GPS, Thermal Printers, 2D & 1D Scanners, Tags & Labels, Sensors), By Technology (RFID/RTLS, GPS, Barcode, Infrared, and Biometrics), By End-User (Food Manufacturers, Warehouse/Pack Farms, Food Retailers, Defense & Security Departments, Other Government Departments, and Others), By Application (Meat & Livestock, Fresh Produce & Seeds, Dairy, Beverages, Fisheries, and Others), and Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Rest of the World) Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth, Trends, Regional Analysis, Competitor Analysis and Forecast 2024-2032.
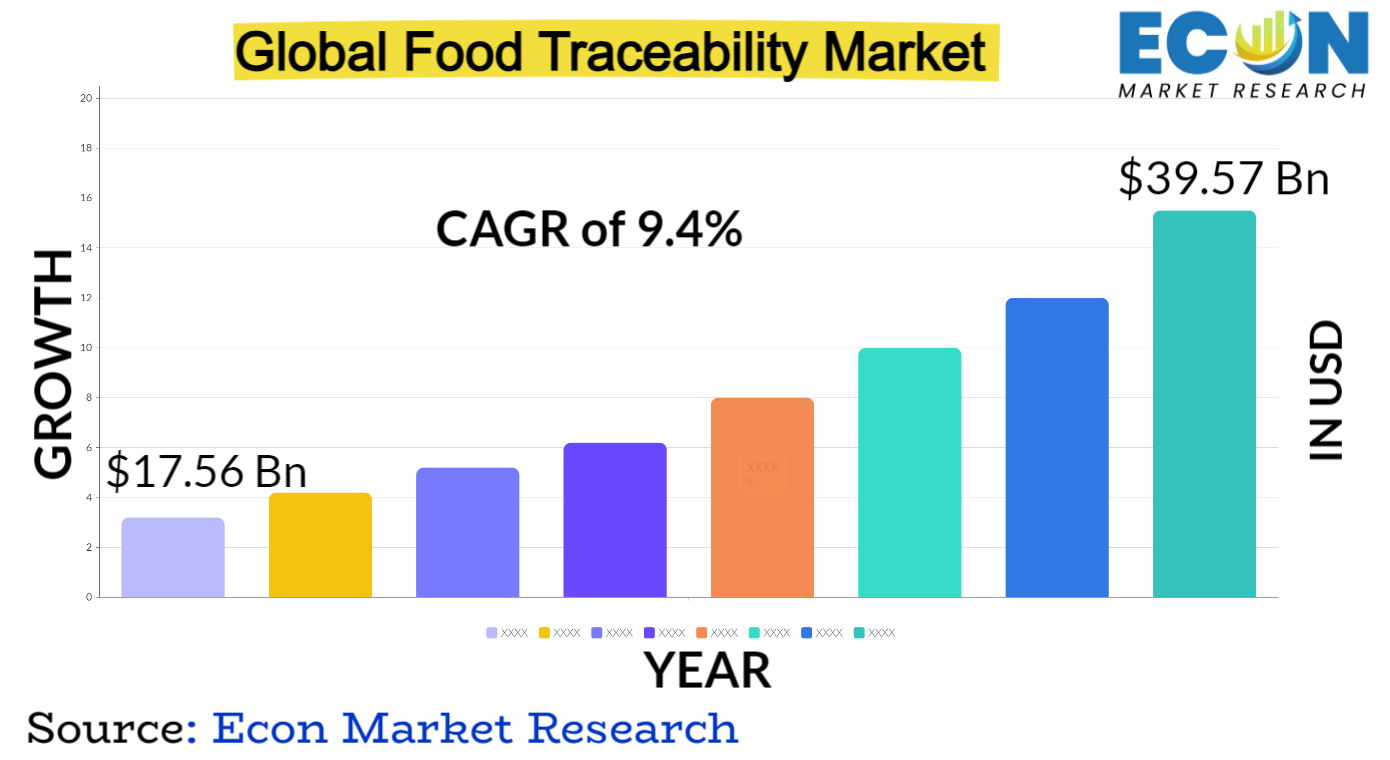
The Food Traceability Market was valued at USD 17.56 billion in 2023 and is estimated to reach approximately USD 39.57 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 9.4% from 2024 to 2032.
In order to guarantee accountability, safety, and transparency throughout the world',s food supply chain, the food traceability industry has become essential. Since its debut, the way that producers, regulators, and consumers view and engage with food items has completely changed. Food traceability makes it easier to track food products from their point of origin to point of consumption by utilizing cutting-edge technology like blockchain, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), and IoT (Inte et of Things). Stakeholders can obtain up-to-date information regarding the product',s origin, manufacturing, processing, and distribution processes using this all-inclusive system.
The adoption of traceability systems has accelerated across industries due to growing conce s about food safety, authenticity, and ethical sourcing. Businesses are using this technology to boost consumer trust, comply with regulations, reduce the risk of fraud or contamination, and eventually increase operational efficiency. A safer and more sustainable food ecosystem is promoted by the incorporation of food traceability, which guarantees a greater degree of accountability while also enabling customers to make knowledgeable decisions about the items they buy.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Estimated Market Value (2023) | 17.56 Bn |
| Projected Market Value (2032) | 39.57 Bn |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Years | 2024 - 2032 |
| Scope of the Report | Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Drivers and Constraints, Historical and Forecast Market Analysis by Segment- By ,Equipment , By Technology, By End-User, By Application, &, Region |
| Segments Covered | By ,Equipment, By Technology, By End-User, By Application, &, Region |
| Forecast Units | Value (USD Billion or Million), and Volume (Units) |
| Quantitative Units | Revenue in USD million/billion and CAGR from 2024 to 2032 |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East &, Africa, and the Rest of World |
| Countries Covered | U.S., Canada, Mexico, U.K., Germany, France, Italy, Spain, China, India, Japan, South Korea, Brazil, Argentina, GCC Countries, and South Africa, among others |
| Report Coverage | Market growth drivers, restraints, opportunities, Porter&rsquo,s five forces analysis, PEST analysis, value chain analysis, regulatory landscape, market attractiveness analysis by segments and region, company market share analysis, and COVID-19 impact analysis. |
| Delivery Format | Delivered as an attached PDF and Excel through email, according to the purchase option. |
Food Traceability Market Dynamics
Key motivators have been rising consumer awareness and demands for food safety, sustainability, and supply transparency. Adoption of traceability technologies is also fueled by gove ment rules and standards that are strict in order to guarantee food safety and quality. Furthermore, industries are investing in strong traceability solutions as a result of increased conce s over the growth in foodbo e illnesses and contamination incidences. Blockchain, RFID, and artificial intelligence are just a few of the technologies that are always evolving in the market and improving traceability capabilities.
By creating end-to-end supply chain visibility, partnerships between manufacturers, retailers, and technology providers propel market expansion. Furthermore, traceability solutions are now more affordable and scalable, opening them up to a wider range of businesses. The food traceability market is growing as consumers want assurance about authenticity, ethical sourcing, and environmental impact. Businesses are using these systems not only for compliance but also as a strategic tool to increase operational efficiency, foster customer trust, and set themselves apart in a crowded market.
Food Traceability Market Drivers
- Consumer Demand for Transparency
This demand is the result of people being more conscious of and conce ed about the environment, ethical sourcing, and food safety. Today',s consumers are more inquisitive and aware of the origins and production processes of the food they eat, as well as the effects it has on the environment and human health. Food scandals, deceptive labeling, and health-related problems have all contributed to a decline in public confidence in the food business, which has intensified the need for transparency. As a result, buyers actively look for guarantees regarding the products', legitimacy, sustainability, and ethical standards.
Businesses have been compelled by this requirement to implement traceability systems, which provide thorough data and visibility across the supply chain, satisfying customer demands and reestablishing confidence. ,Customers', increasing need for transparency is influencing the market and pressuring businesses to promote accountability, openness, and honesty in their food production operations as they become more knowledgeable and empowered consumers.
- Technological Advancements
,The development of technologies such as blockchain, RFID, IoT, and AI has completely changed the way food goods are tracked, traced, and managed across the supply chain. With their ability to provide real-time visibility, accurate data, and seamless integration across the intricate network of food production and distribution, these innovations provide strong answers to persistent problems. For example, blockchain ensures clear and unchangeable records, improving security and confidence when tracking the sources of food. Reducing spoilage and guaranteeing quality, RFID and IoT sensors allow for exact tracking and monitoring of temperature, location, and conditions.
Artificial intelligence (AI)-powered analytics collect enormous volumes of data and provide useful insights for better risk and decision-making. The combination of these developments enables end-to-end traceability, enabling stakeholders to react quickly to problems such as fraud, contamination, or supply chain interruptions. , These technologies are driving innovation in the food business by making traceability less of a compliance-driven requirement and more of a strategic tool for improving customer trust, safety, and sustainability. As they develop, they become more widely available and affordable.
Restraints:
- Implementation Costs and Infrastructure
The initial outlay necessary to incorporate these systems into current infrastructures can be high, especially for startups or companies using antiquated technology. In addition to purchasing the required hardware and software, there are other expenditures involved such as staff training, process reconfiguration, and possible disruptions during the integration stage. Costs are further increased by the requirement for standardized protocols and system compatibility throughout the supply chain. This expensive expense frequently serves as a barrier to adoption, particularly for smaller firms, making comprehensive traceability solutions unaffordable for them.
Furthermore, longer implementation times may result from the complexity of infrastructure improvements or overhauls in larger businesses, which would postpone the benefits of traceability. Therefore, even while there are clear potential benefits to traceability, the high implementation costs and infrastructure challenges continue to be significant obstacles that prevent the smooth adoption of these systems throughout the food industry.
- Complexity in Integration and Adoption
It can be extremely difficult to integrate new traceability technologies into already-existing infrastructures, particularly for businesses with complex, well-established supply chains. There may be compatibility problems and disruptions throughout the integration phase due to the wide variety of systems, software, and procedures currently in place. Beyond only the technical, this complexity includes workforce training and corporate change management. Workers may become resistant to new workflows, technologies, and data management procedures, which could result in decreased productivity and extra training expenses.
A supply chain',s numerous stakeholders, each with their own set of procedures and technological capabilities, must be integrated seamlessly, which adds layers of complexity that may prevent adoption from happening quickly and effectively. Therefore, this complexity serves as a major barrier that slows down adoption and prevents the industry from completely embracing traceability systems, even in spite of the potential benefits.
Opportunities:
- Emergence of Advanced Technologies
The food supply chain now has never-before-seen opportunities to improve transparency, efficiency, and trust because to innovations like blockchain, IoT, AI, and RFID. The unchangeable and transparent ledger system of blockchain guarantees safe and impenetrable documentation of each step of food production and delivery. Real-time environmental condition monitoring is made possible by IoT devices and sensors, which also ensure optimal storage and transportation, lower waste, and improve product quality. Large-scale databases are tapped into by AI-driven analytics, which then delivers useful information to reduce risks, forecast demand, and optimize operations.
End-to-end traceability is made possible by the combination of various technologies, providing consumers and stakeholders with comprehensive and easily accessible information regarding the provenance, quality, and sustainability of food. Furthermore, these technologies democratize access by making advanced traceability solutions accessible to organizations of all sizes as they develop and become more reasonably priced and user-friendly. This wave of technology not only raises industry standards but also encourages innovation, opening the door for a food ecosystem that is more open, effective, and focused on the needs of consumers.
- Consumer Demand for Ethical Sourcing
Mode consumers place a higher value on food',s ethical and environmental implications in addition to its quality and flavor. Because of this trend in consumer awareness, traceability systems have an opportunity to live up to these expectations by offering comprehensive insights into food items', whole lifespan, from farm to table. Companies can use these systems to openly demonstrate their commitment to ethical sourcing standards, including fair trade, organic farming, compassionate treatment of animals, and ecologically sustainable production techniques.
Furthermore, traceability systems provide a direct conduit for communicating these values to consumers, who are looking for authenticity and confidence in the provenance of their food, strengthening the bond between the consumer and the brand. Customers are better equipped to make decisions that are consistent with their values when they can independently check claims made about sustainability, fair labor standards, and ecological effect. Therefore, adopting traceability and ethical sourcing to suit customer demands also gives businesses a competitive edge, promotes innovation, and helps the food industry become more sustainable and socially conscious.
Segment Overview
- By Equipment
Based on equipment, the global food traceability market is divided into PDA with GPS, thermal printers, 2D &, 1D scanners, tags &, labels, sensors. The 2D &, 1D scanners category dominates the market with the largest revenue share in 2023. The tools used to read and decode barcodes or QR codes on labels or packaging are called scanners. While 2D scanners are capable of reading more complicated QR codes or two-dimensional barcodes, 1D scanners are only able to read conventional linear barcodes. These scanners are essential for obtaining and deciphering data encoded on labels, helping to identify goods, following their path, and documenting important details all the way through the supply chain.
PDAs with GPS are portable computers used in the food supply chain for tracking, inventory control, and data collection. These sensors enable exact monitoring of product transportation and storage conditions by combining real-time data gathering and GPS location tracking. PDAs with GPS are useful instruments for tracking the origins of products, guaranteeing precise delivery routes, and keeping track of storage and transit specifics. Labels and tags with vital information like product specifications, barcodes, expiration dates, and batch numbers are produced using thermal printers. These printers employ heat to create long-lasting, premium labels that can tolerate a range of environmental factors in the food supply chain.
In order to accurately track and trace food goods, thermal printers are essential for printing barcode labels that are scanned at several checkpoints. Physical markers attached to food packaging or goods, tags and labels hold vital information necessary for traceability. Data like the product',s origin, date of manufacture, date of expiration, batch number, and occasionally QR or barcodes are included on these labels. The main tools for encoding data that can be scanned and followed throughout the supply chain are tags and labels. Sensors are gadgets that are included into storage or packaging systems to keep an eye on variables like humidity, temperature, and other elements that may affect the safety and quality of food.
- By Technology
Based on the technology, the global food traceability market is categorized into RFID/RTLS, GPS, barcode, infrared, and biometrics. The RFID/RTLS category leads the global food traceability market with the largest revenue share in 2023. Radio waves are used by RFID technology to identify and track tags affixed to goods or things. RFID tags have unique data that can be wirelessly read by RFID readers, enabling automatic, real-time data collection without the need for line-of-sight scanning. A subtype of RFID called RTLS is dedicated to tracking and locating objects in a predetermined area in real time.
Accurate logistics tracking, supply chain product movement monitoring, and inventory management are made possible by RFID/RTLS systems. , In order to pinpoint the exact geographic location of objects or cars fitted with GPS receivers, GPS technology employs satellite signals. , ,GPS is used to track and monitor the movement of items across various supply chain stages in the context of food traceability. Barcodes are optical data representations that can be read by machines, they usually take the shape of parallel lines that vary in width. Barcode readers can scan and decipher the information included in these codes, which are distinctive to the product.
Food traceability uses barcodes extensively to encode data like product identification, batch numbers, expiration dates, and more. Temperature monitoring and control in food storage and transportation are accomplished through the use of infrared technology. Without making physical contact, infrared sensors can measure surface temperatures and identify heat signatures. , Utilizing distinct biological traits for identification and authentication, such as fingerprints, retinal scans, or facial recognition, is known as biometric technology. Biometrics may be integrated for access control and authentication at particular supply chain checkpoints to guarantee security and authenticity, even if they are less frequently employed in food traceability.
- By End-User
Based on end-user, the global food traceability market is segmented into food manufacturers, warehouse/pack farms, food retailers, defense &, security departments, other gove ment departments, and others. The food manufacturers segment dominates the food traceability market. This category comprises businesses that produce, process, and manufacture food. Systems for tracking raw supplies, production processes, and final products are used by food makers. Maintaining quality standards, locating contamination sources, and guaranteeing legal compliance are all made easier with traceability.
Before food is distributed, warehouses and pack farms are essential for handling, storing, and packaging food items. ,In order to preserve product integrity, traceability systems in this market segment help with inventory management, tracking storage conditions, and keeping an eye on the flow of goods within the facilities. Supermarkets, grocery stores, eateries, and other businesses that sell food to customers are considered food retailers. Retailers benefit from traceability systems because they help with inventory management, product freshness assurance, and informing customers about the origin and caliber of products.
Departments of defense and security concentrate on using traceability systems to guarantee food safety in supply chains connected to the military or the gove ment. Traceability is useful for controlling inventories, keeping an eye on rations, and making sure that strict safety regulations are followed in delicate situations. Beyond the departments of defense and security, other gove ment agencies use traceability systems to monitor food safety, enforce laws, and carry out inspections to protect the public',s health and guarantee adherence to food safety standards. Examples of these agencies include health, agriculture, and regulatory bodies.
- By Application
Based on application, the global food traceability market is divided into meat &, livestock, fresh produce &, seeds, dairy, beverages, fisheries, and others. The meat &, livestock scanners category dominates the market with the largest revenue share in 2023. This category includes all forms of meat traceability in the meat business, including beef, pork, chicken, and other livestock. In this industry, traceability refers to keeping an eye on an animal',s entire existence, including its breeding, feeding, health, transit, and processing. It guarantees that meat products satisfy quality requirements, follow safety guidelines, and tell customers about the origin and care of the animal.
Fruits, vegetables, grains, and seeds intended for planting or ingestion are all considered fresh produce and seeds. In this area, traceability refers to keeping an eye on farming operations, from planting seeds to harvesting, packing, and distributing them. By monitoring elements including farming practices, pesticide use, storage conditions, and handling protocols, it guarantees the integrity and safety of fresh produce. Traceability is an issue in the dairy industry when it comes to the manufacturing and processing of dairy products like cheese, yogurt, and milk.
In the dairy industry, traceability refers to keeping an eye on every step of the supply chain, including the welfare and diet of dairy cows as well as the gathering, processing, packing, and distribution of milk. It guarantees the safety, quality, and adherence to dairy regulations of the product. The beverage category, which includes bottled water, soft drinks, juices, and alcoholic beverages, addresses traceability in the beverage sector. Traceability in beverage production entails keeping an eye on ingredients, bottling, labeling, distribution, and labeling procedures to guarantee product quality, safety, and legal compliance. Monitoring the origin, handling, and distribution of seafood items derived from fishing operations is known as ",fisheries traceability.",
Food Traceability Market Overview by Region
The global food traceability market is categorized into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Rest of the World. North America emerged as the leading region, capturing the largest market share in 2023. The region',s dominance is ascribed to its strong infrastructure, technological capabilities, and strict regulatory framework that places a high priority on food quality and safety. Mode traceability technologies like RFID, blockchain, and sophisticated tracking systems have been widely adopted by advanced economies like the US and Canada. This adoption has been especially widespread in the fresh produce, dairy, meat and cattle, and beverage sectors of the food business. As a result of the region',s technological innovation leadership, consumer-driven transparency demands, and legislative efforts, North America has established itself as a pioneer in the development and application of extensive food traceability systems.
Over the course of the projection period, the Asia-Pacific area is expected to experience the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR). Food product consumption is expanding in this region due to fast urbanization, population growth, and rising disposable incomes. Furthermore, regulatory activities and growing conce s about food safety are driving the adoption of traceability solutions. Furthermore, the growing e-commerce industry and technology developments are increasing the need for transparent supply chains. As an example, Walmart China launched a blockchain-based traceability platform in December 2020 as a component of their product traceability initiative. Customers can obtain extensive information about the goods, such as delivery schedules, test results, location updates, transportation procedures, and other pertinent details at every level of the supply chain, by simply scanning the QR code.
Food Traceability Market Competitive Landscape
In the global food traceability market, a few major players exert significant market dominance and have established a strong regional presence. These leading companies remain committed to continuous research and development endeavors and actively engage in strategic growth initiatives, including product development, launches, joint ventures, and partnerships. By pursuing these strategies, these companies aim to strengthen their market position, expand their customer base, and capture a substantial share of the market.
Some of the prominent players in the global food traceability market include,
- Motorola Solutions, Inc.
- SGS SA
- CH Robinson Worldwide Inc.
- Inte ational Business Machines Corporation
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc
- E. I. Du Pont de Nemours and Company
- Cognex Corporation
- Zebra Technologies Corporation, and various others.
Food Traceability Market Recent Developments
- In Sepetember 2023, A tech-enabled traceability solution was announced by iFoodDS and IBM to assist businesses in the food supply chain in complying with the FDA',s Food Traceability Rule, or FSMA 204(d). The new solution, iFoodDS Trace ExchangeTM (with IBM Food TrustTM), builds on decades of experience in food traceability software and will meet supplier needs and enterprise scalability demands.
- In March 2023, TOMRA has strategically invested in Kezzler, a company that provides product serialization and traceability, to acquire a 14% ownership position. The investment was made by purchasing secondary shares and taking part in the company',s rights issuance.
- In May 2022, Optchain is a set of modular intelligent supply chain (ISC) solutions created specifically for the food and beverage industry. OPTEL Group is a global leader in supply chain traceability solutions across several industries. With Optchain, all parties involved in the supply chain will be able to comply with the Food and Drug Administration',s recent revision to the Food Safety Mode ization Act (FSMA), particularly Section 204. This is because Optchain is designed with this goal in mind.
- In December 2020, Rebellion Photonics (US) is acquired by Honeywell (US). Innovative, intelligent, visual gas monitoring solutions that maximize safety, operational performance, emissions mitigation, and compliance in the petrochemical, power, and oil and gas sectors are offered by Rebellion Photonics, a Houston-based company.
Food Traceability Market Report Segmentation
| ATTRIBUTE | , , , , DETAILS |
| By Equipment |
|
| By Technology |
|
| By End-User |
|
| By Application |
|
| By Geography |
|
| Customization Scope |
|
| Pricing |
|
,
No FAQs available.
Report Details
- Published Date:Dec 27, 2023
- Format:PDF
- Language:English
- Delivery:Instant
Download Sample
Get a free sample report to preview the content and quality.
